Future Look of Iraq Complicated by Internal Migration
By JAMES GLANZ and ALISSA J. RUBIN
Published: September 19, 2007
BAGHDAD, Sept. 18 — A vast internal migration is radically reshaping Iraq’s ethnic and sectarian landscape, according to new data collected by thousands of relief workers, but displacement in the most populous and mixed areas is surprisingly complex, suggesting that partitioning the country into semiautonomous Sunni, Shiite and Kurdish enclaves would not be easy.
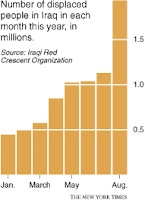
The migration data, which are expected to be released this week by the Iraqi Red Crescent Organization but were given in advance to The New York Times, indicate that in Baghdad alone there are now nearly 170,000 families, accounting for almost a million people, that have fled their homes in search of security, shelter, water, electricity, functioning schools or jobs to support their families.
The figures show that many families move twice, three times or more, first fleeing immediate danger and then making more considered calculations based on the availability of city services or schools for their children. Finding neighbors of their own sect is just one of those considerations.
Over all, the patterns suggest that despite the ethnic and sectarian animosity that has gripped the country, at least some Iraqis would rather continue to live in mixed communities.
The Red Crescent compiled the figures from reports filed as recently as the end of August by tens of thousands of relief workers scattered across all parts of Iraq who are straining to provide aid for an estimated 280,000 families swept up nationwide in an enormous and complex migration.
A bird’s-eye view of the data suggests that since the bombing of a revered Shiite mosque in February 2006 triggered severe sectarian strife, Sunnis generally have been moving north and west, Shiites south, and Christians to the far north. But the picture in the mixed and highly populous center of the country is, if anything, becoming more complicated.
It is this mixed population center, the often violent interface between more homogeneous Sunni and Shiite regions, that some advocates of partition have suggested would separate into more homogeneous areas as Iraqis seek safety among members of their own sects.
But the new figures show that the migration is not neatly dividing Baghdad along the Tigris, separating Sunnis who live predominantly on the west bank from Shiites, who live predominantly on the east. Instead, some Sunnis are moving to the predominantly Shiite side of the river, into neighborhoods that are relatively secular, mixed and where services are better, according to Red Crescent staff.
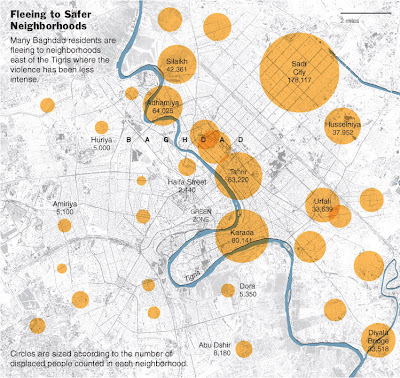
Just last week within Baghdad itself, a Sunni tribe of 250 families that lived in Dora, one of the most violent neighborhoods, was forced to flee. Rather than going to an area where they would be with others of their sect, they went to their neighbors to the south, in Abu Dshir, a Shiite area. They were welcomed by the local tribe and given places to stay in people’s homes, according to field staff both for the Red Crescent and the International Organization for Migration, an intergovernmental agency.
Still, some poor Iraqis, for example those fleeing ethnic cleansing by Al Qaeda in Mesopotamia in villages in the eastern province of Diyala, make the only choice available to them: head for Baghdad and stop in one of the refugee camps on the fringes of the city amid the other desperately poor.
 The size and scope of the migration has elicited deep concern on the part of aid officials. Relief workers “have a mammoth task to alleviate the sufferings of this vast number of Iraqis,” a draft report on the Red Crescent figures says.
The size and scope of the migration has elicited deep concern on the part of aid officials. Relief workers “have a mammoth task to alleviate the sufferings of this vast number of Iraqis,” a draft report on the Red Crescent figures says.Although Iraqis of every income level, sect, ethnicity and region of the country have been caught up in this migration, perhaps the most tragic consequences turn up where enormous numbers of poor Iraqi villagers have collected in camps, shantytowns and urban slums after leaving behind almost everything they owned, said Dr. Said Hakki, a physician who is the president of the Red Crescent.
“It’s tragic, absolutely tragic,” Dr. Hakki said. “I have been a surgeon all my life, and I have seen death many times; that never scared me, never shook me. But when I saw the toll here in Iraq,” he said, referring to the groups of displaced people, “that definitely shook me.”
“How could a human let human beings suffer so much for so long?” Dr. Hakki said.
Continued
No comments :
Post a Comment